Instructor : Tom Igoe
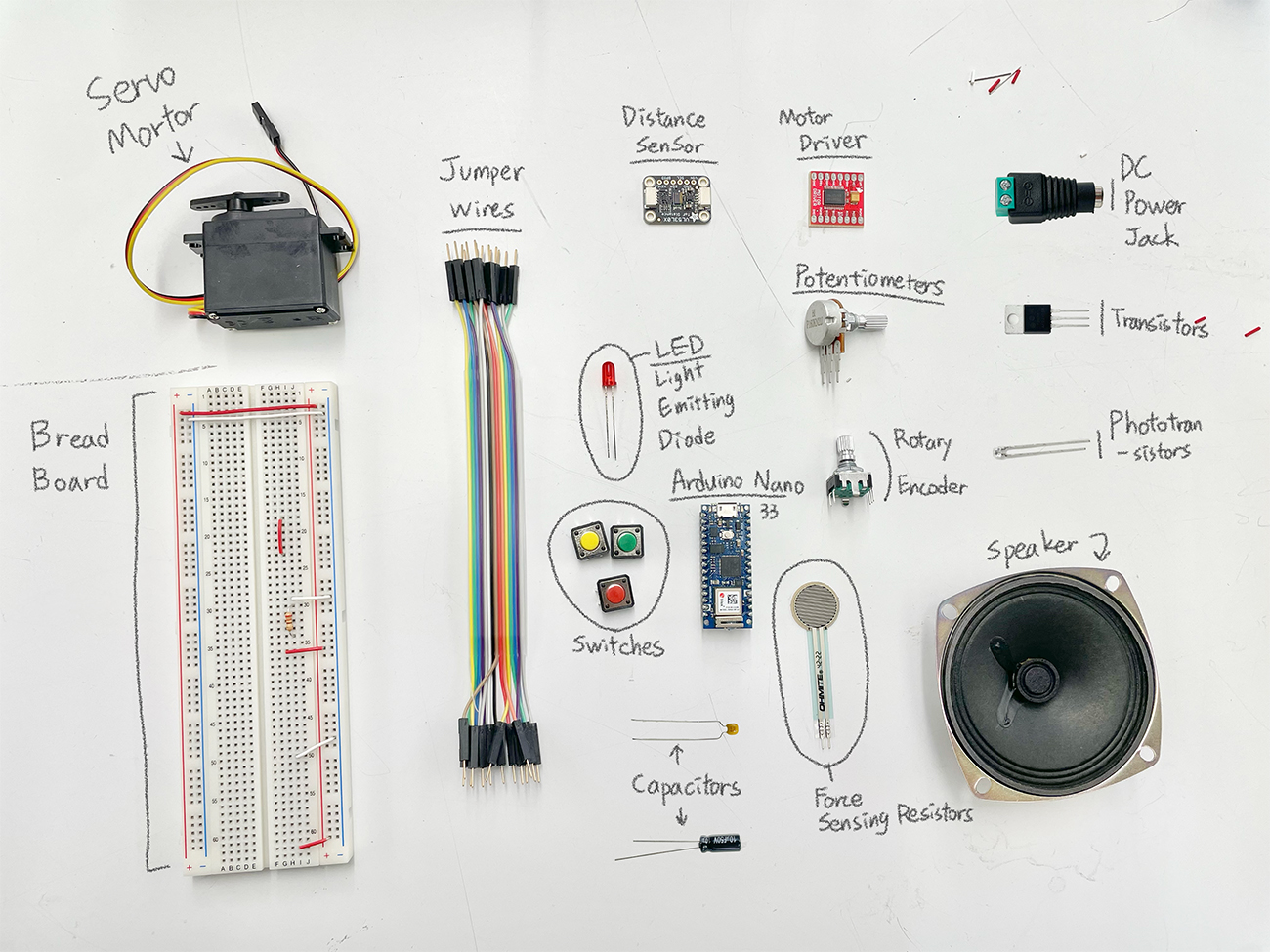
Lab: Components
Basic Concepts of Electricity:
- Electricity is the flow of electrical energy through conductive materials.
- An electrical circuit consists of a power source and components that convert electrical energy into other forms of energy.
- Current (I – Intensity of Current) is crucial in electrical circuits. Setting the appropriate voltage (V) and resistance (R) to achieve the desired current is important.
Key Terms:
- Voltage: Potential difference, measured in volts (V)
- Current: Flow of electrons, measured in amperes (A)
- Resistance: Opposition to electrical flow, measured in ohms (Ω)
- Ohm’s Law: V = I × R
Main Components:
- Resistors: Control the flow of current
- Capacitors: Store and release electrical energy
- Diodes: Allow current flow in only one direction
- Transistors and Relays: Electrical switching devices
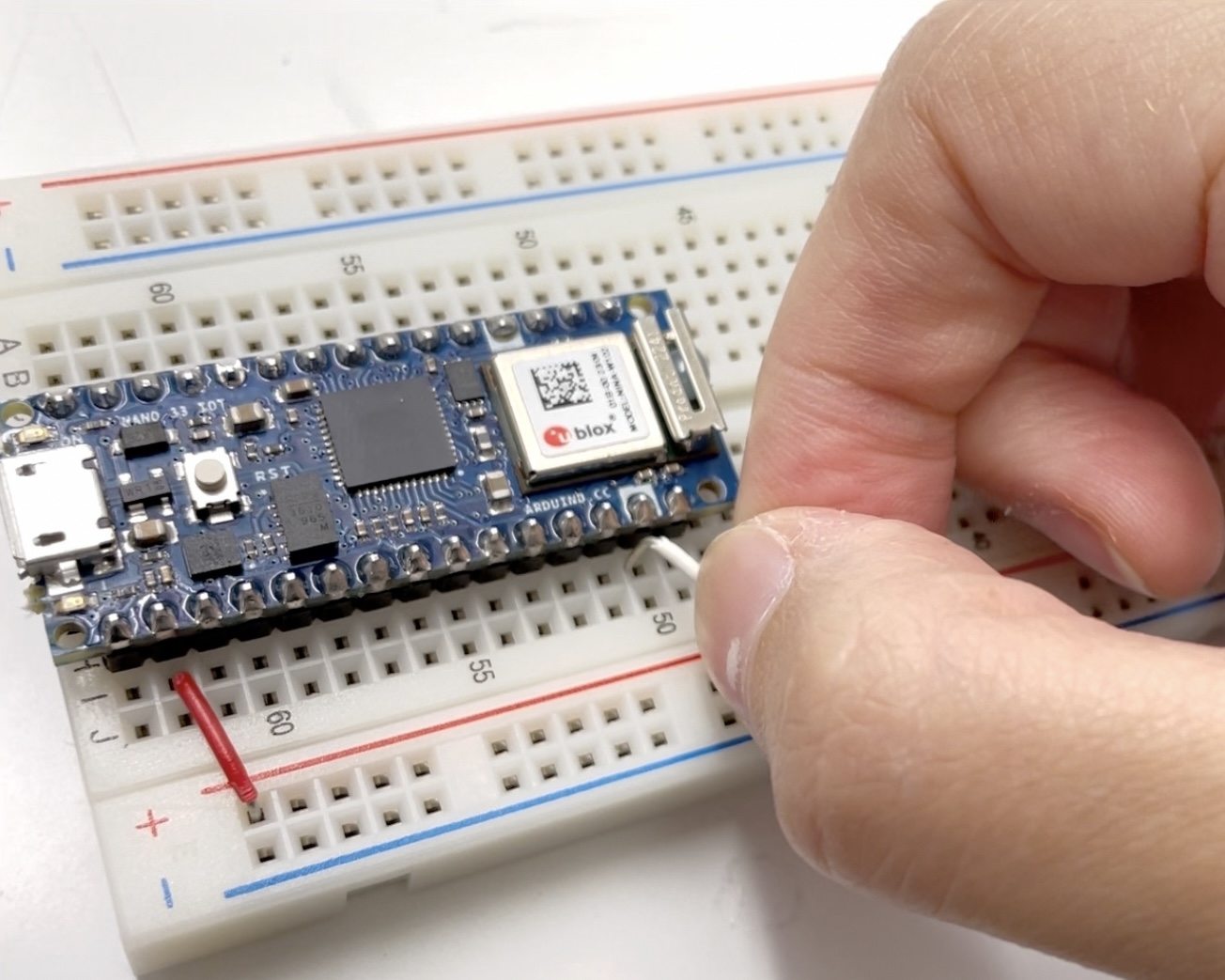
Lab: Setting Up A Breadboard
Get power from the circuit via a microcontroller like the Arduino Nano 33 IoT (or the Uno).
Microcontroller & Breadboard : 3.3V connected to the red voltage bus(+), Ground connected to the blue ground bus(-)
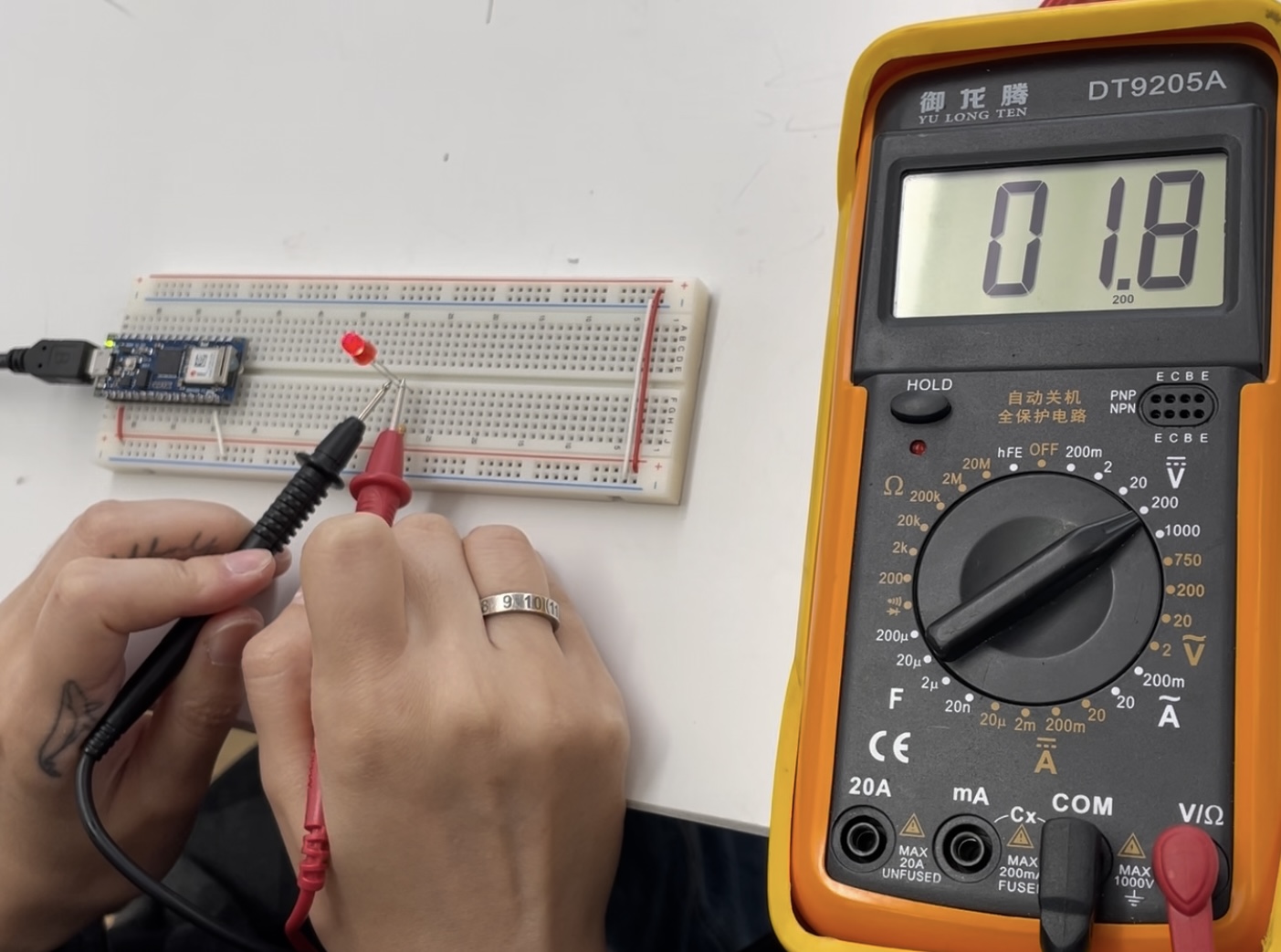
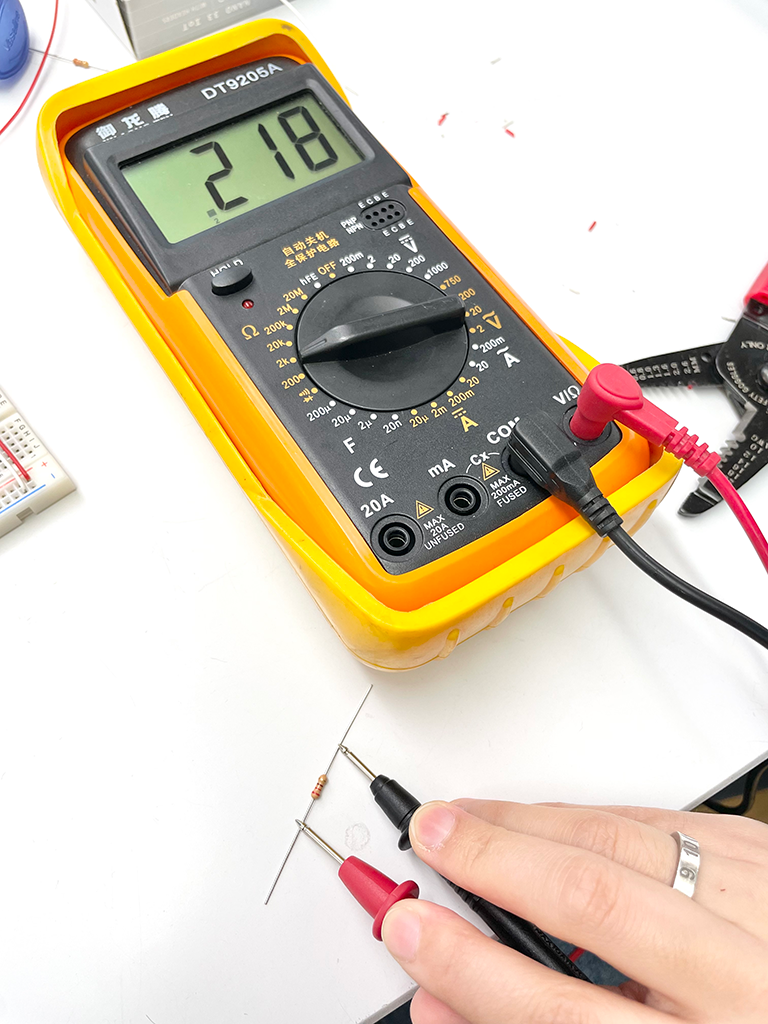
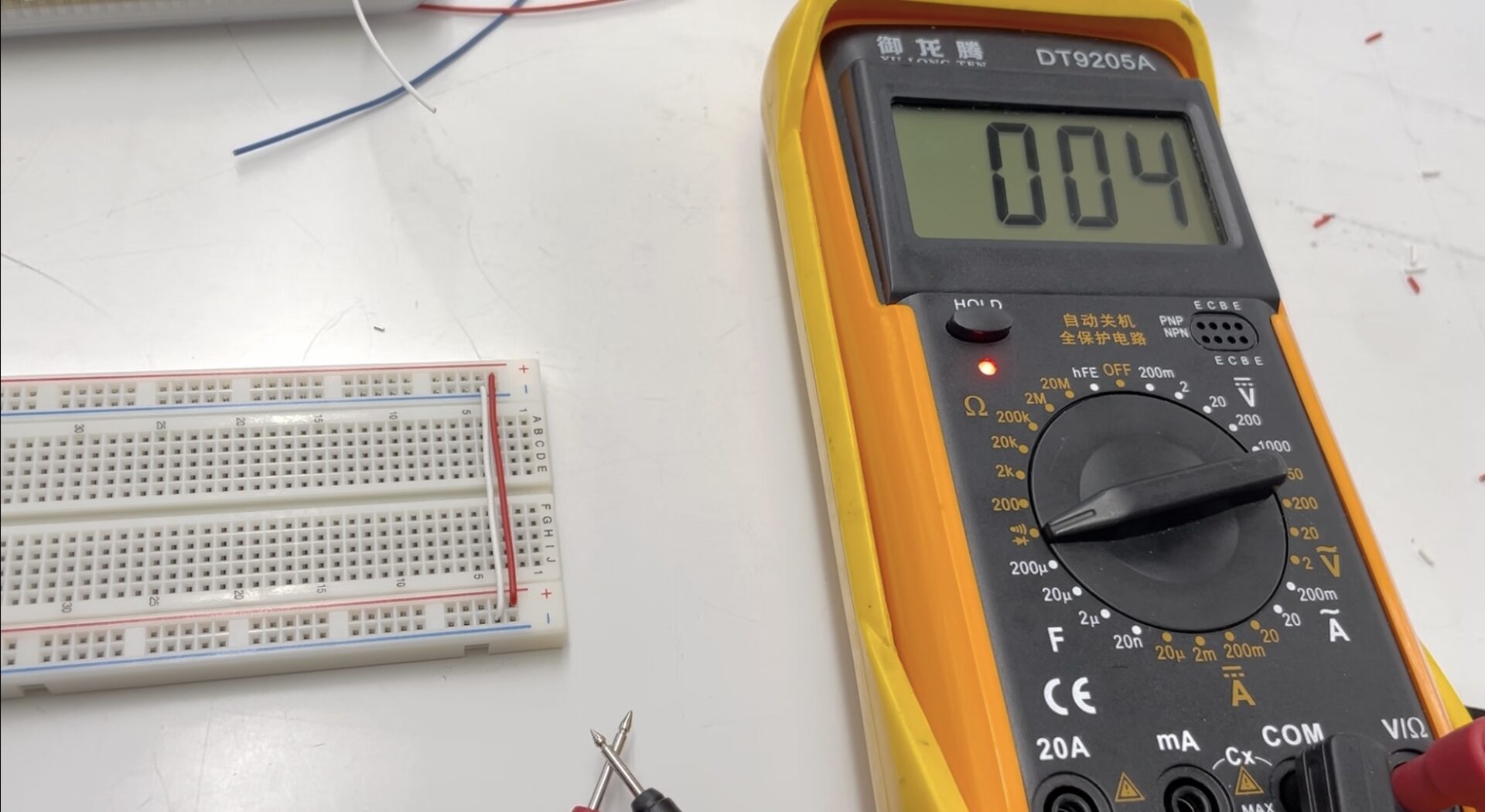
Lab: Electronics and using a Multimeter
The meter measures continuity. When continuity is detected, it emits a beep sound.


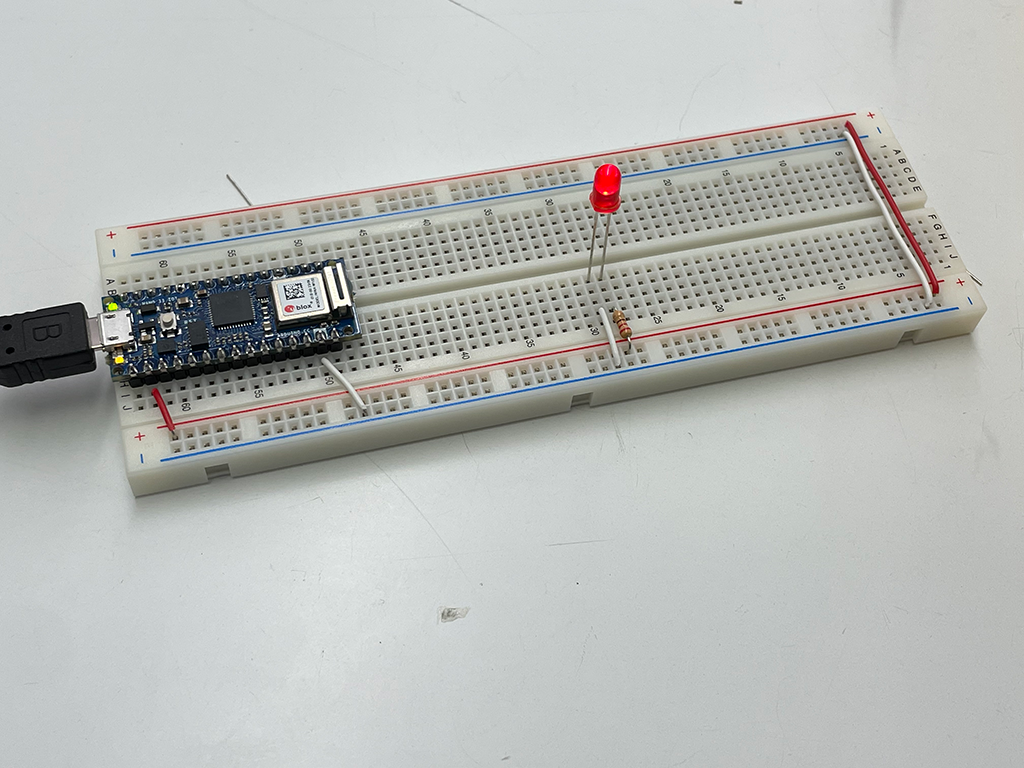
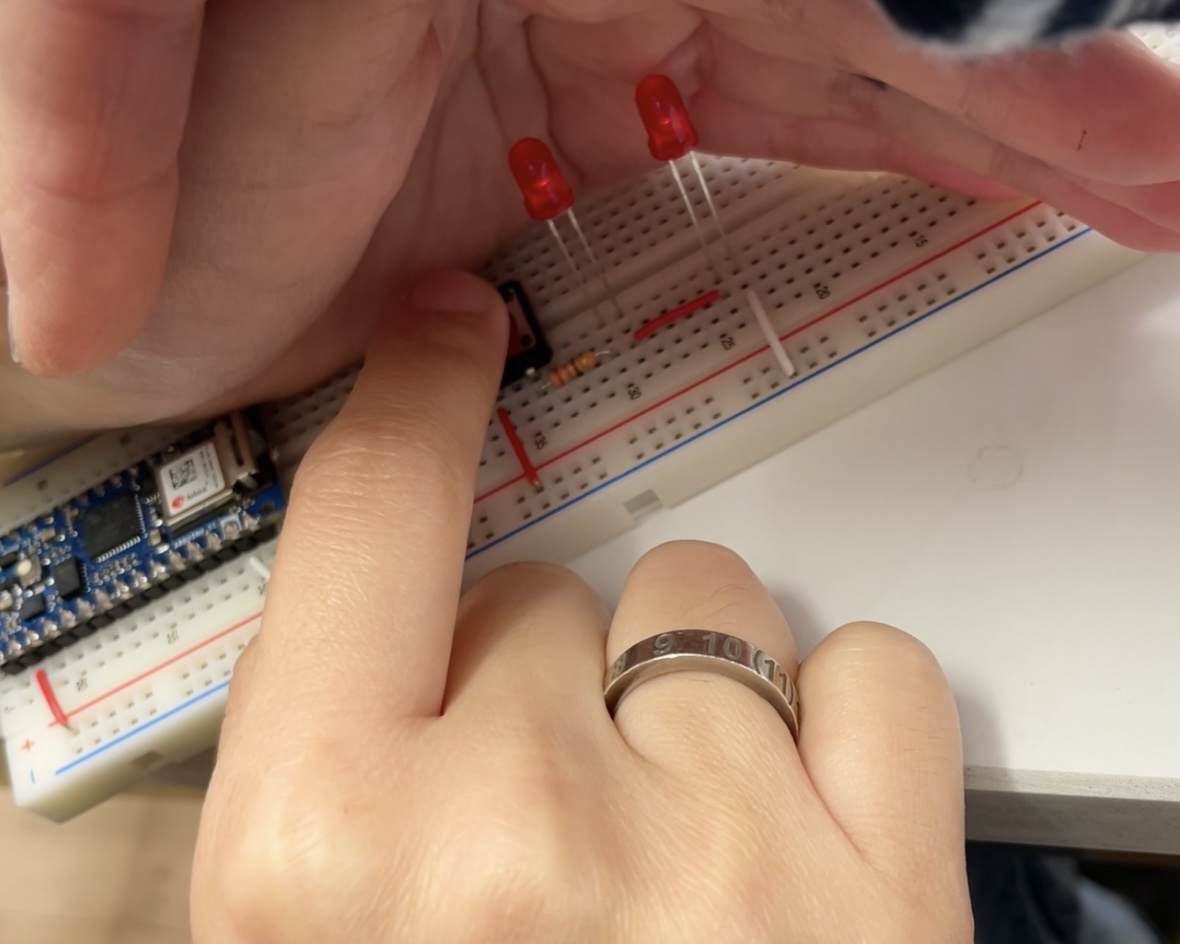
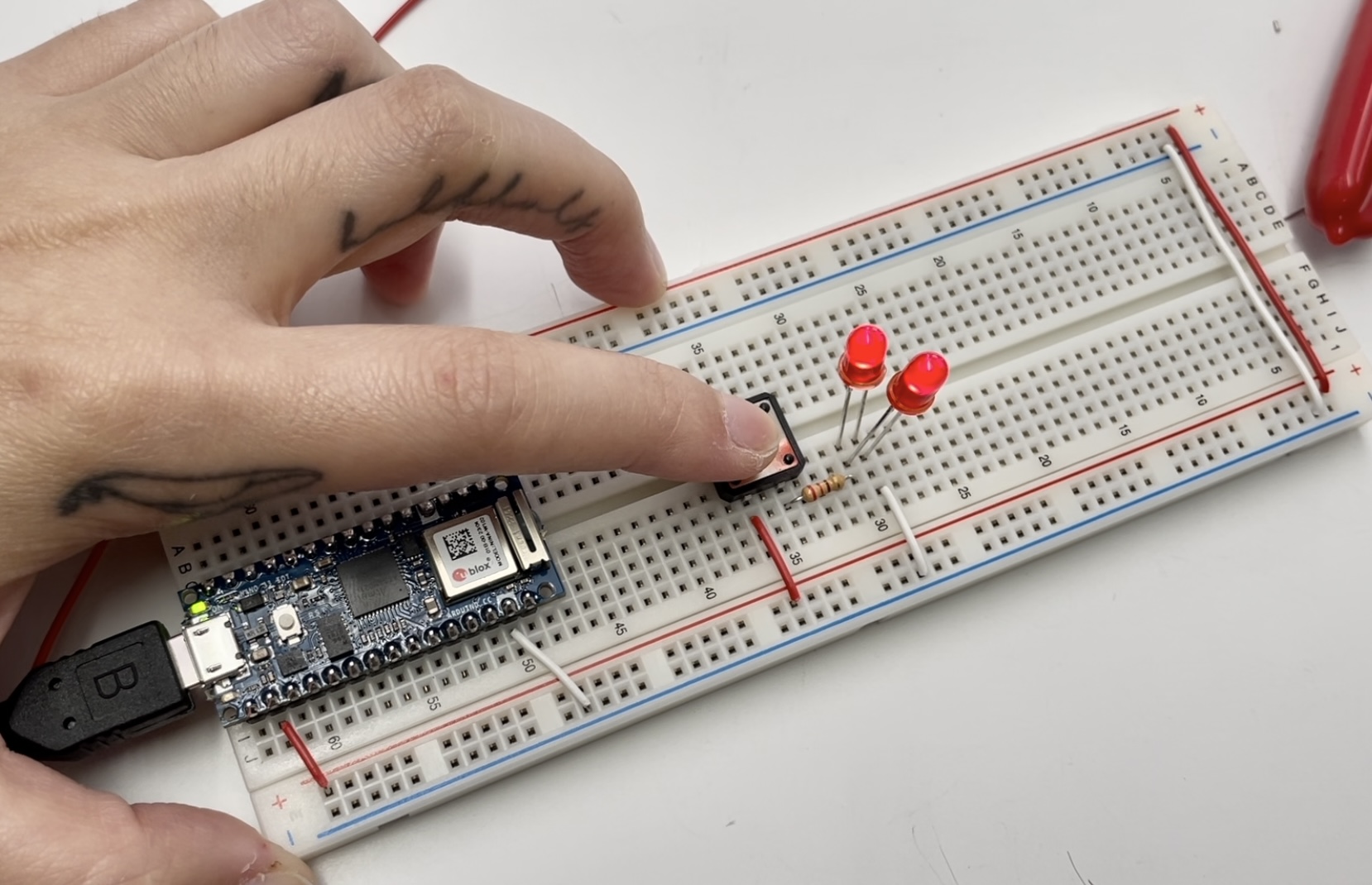
A Switched LED Circuit
Check the circuit diagrams for LEDs connected in series and parallel
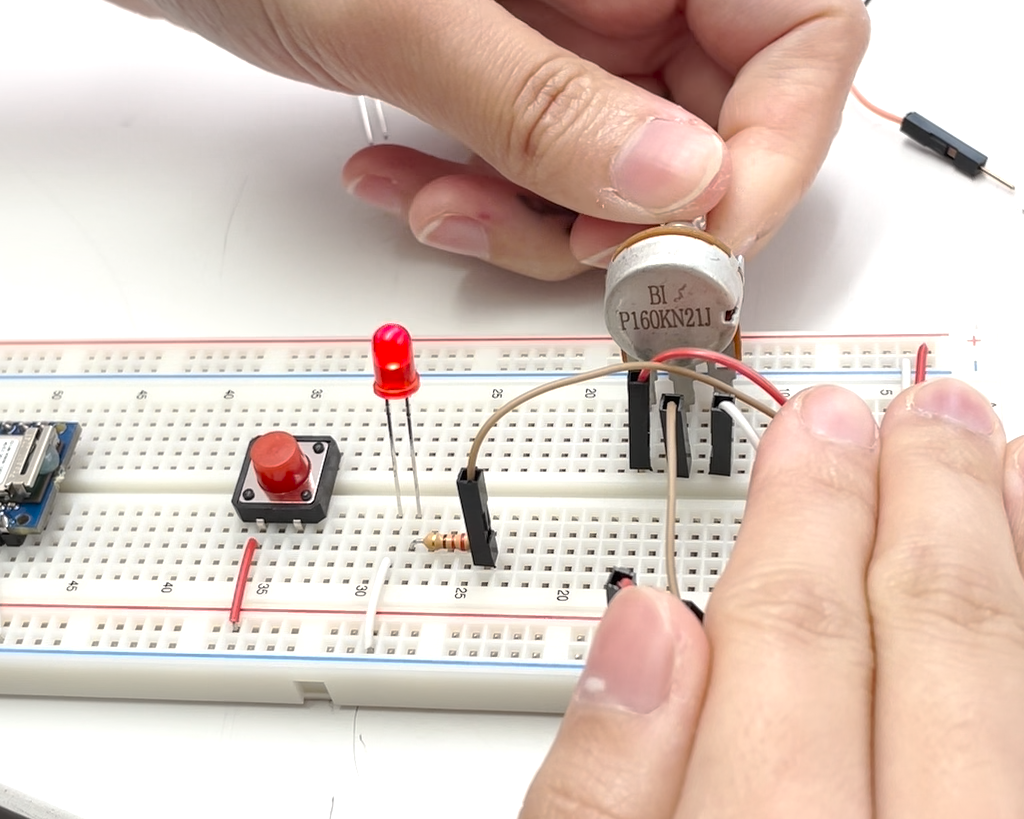
Voltage with a Potentiometer
By adjusting the resistance value using a potentiometer, the LED’s light dims and brightens.
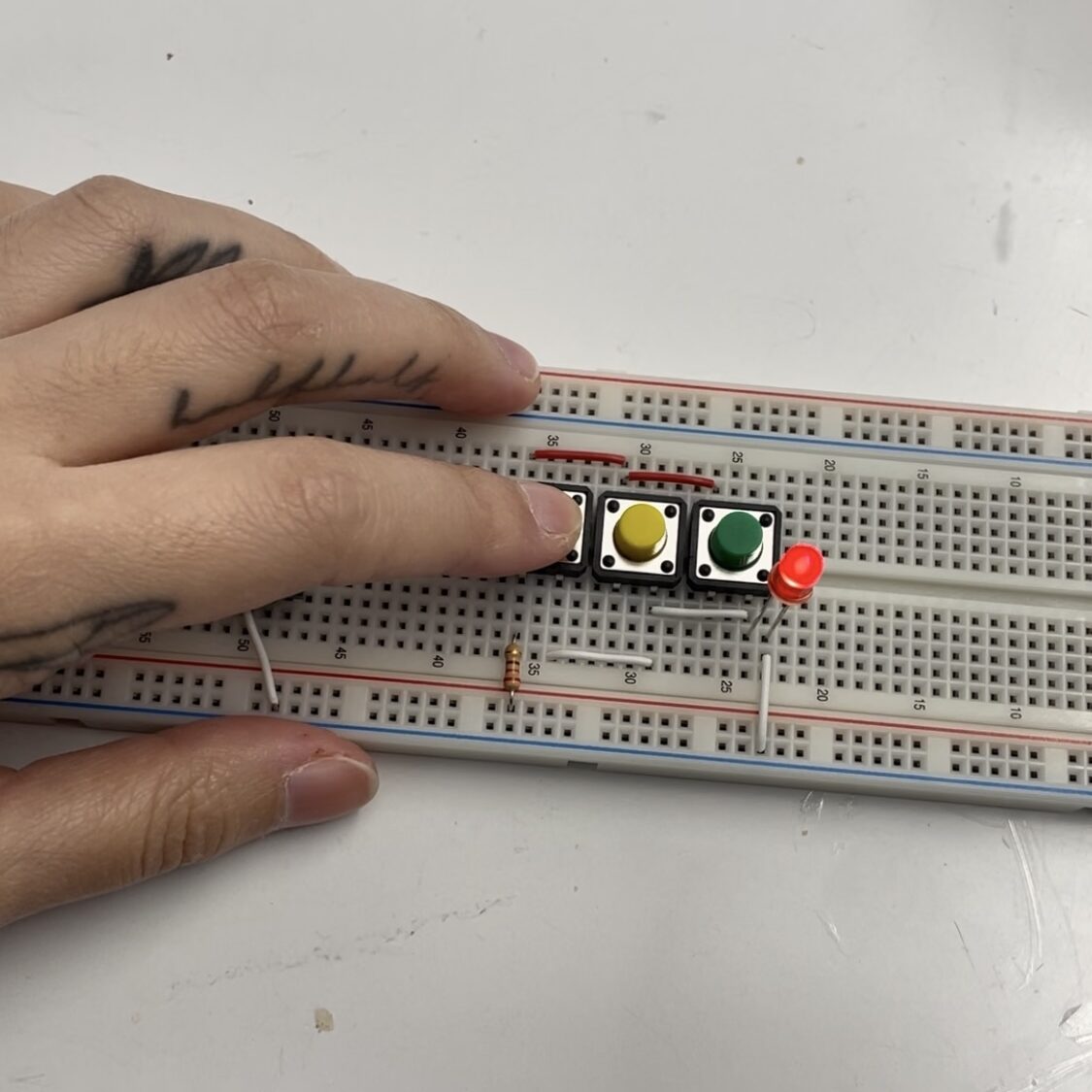
Lab: Switches and Pushbuttons
Three switches in parallel
Make a circuit with 3 Tactile Switches connected and pressing any button turns on the LED.
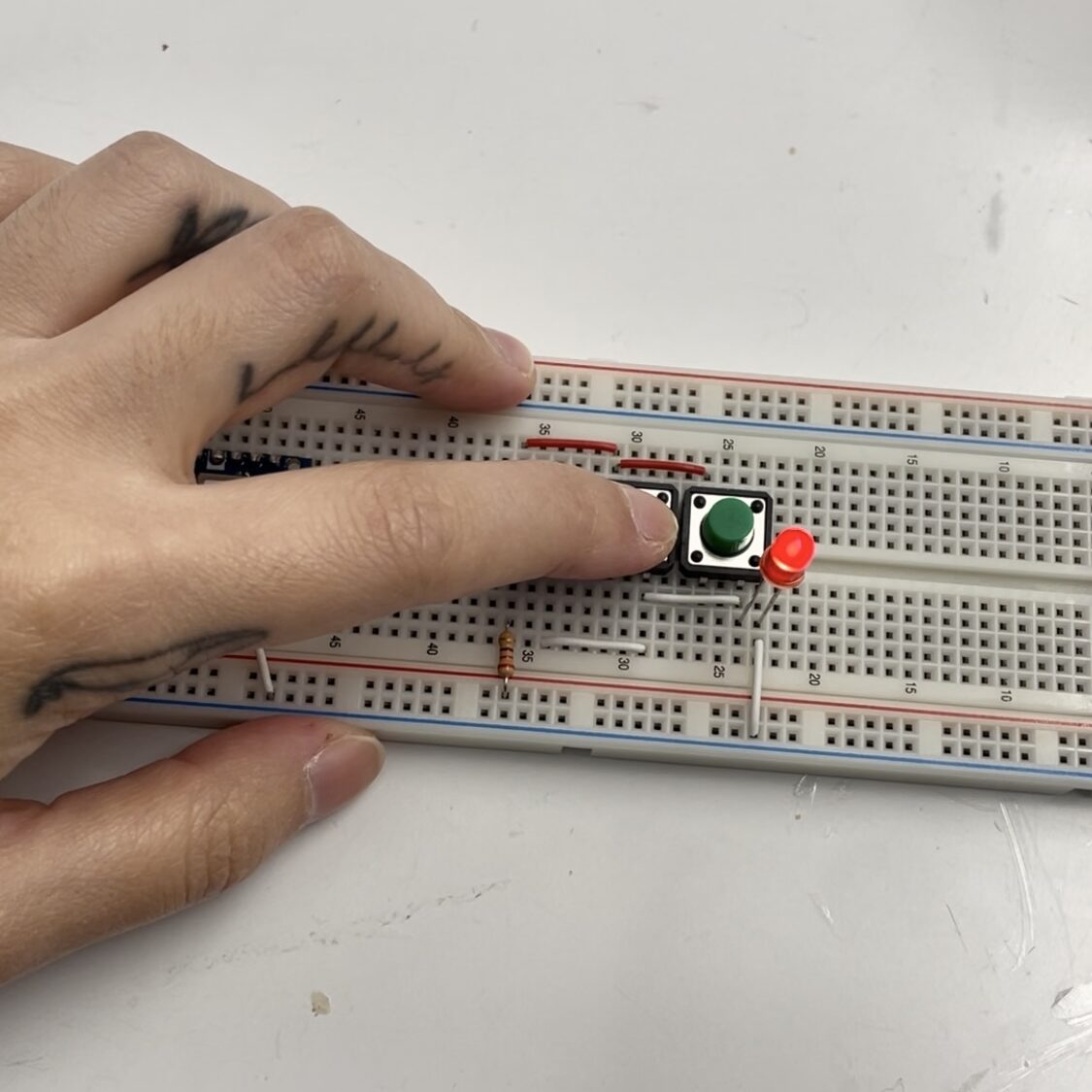
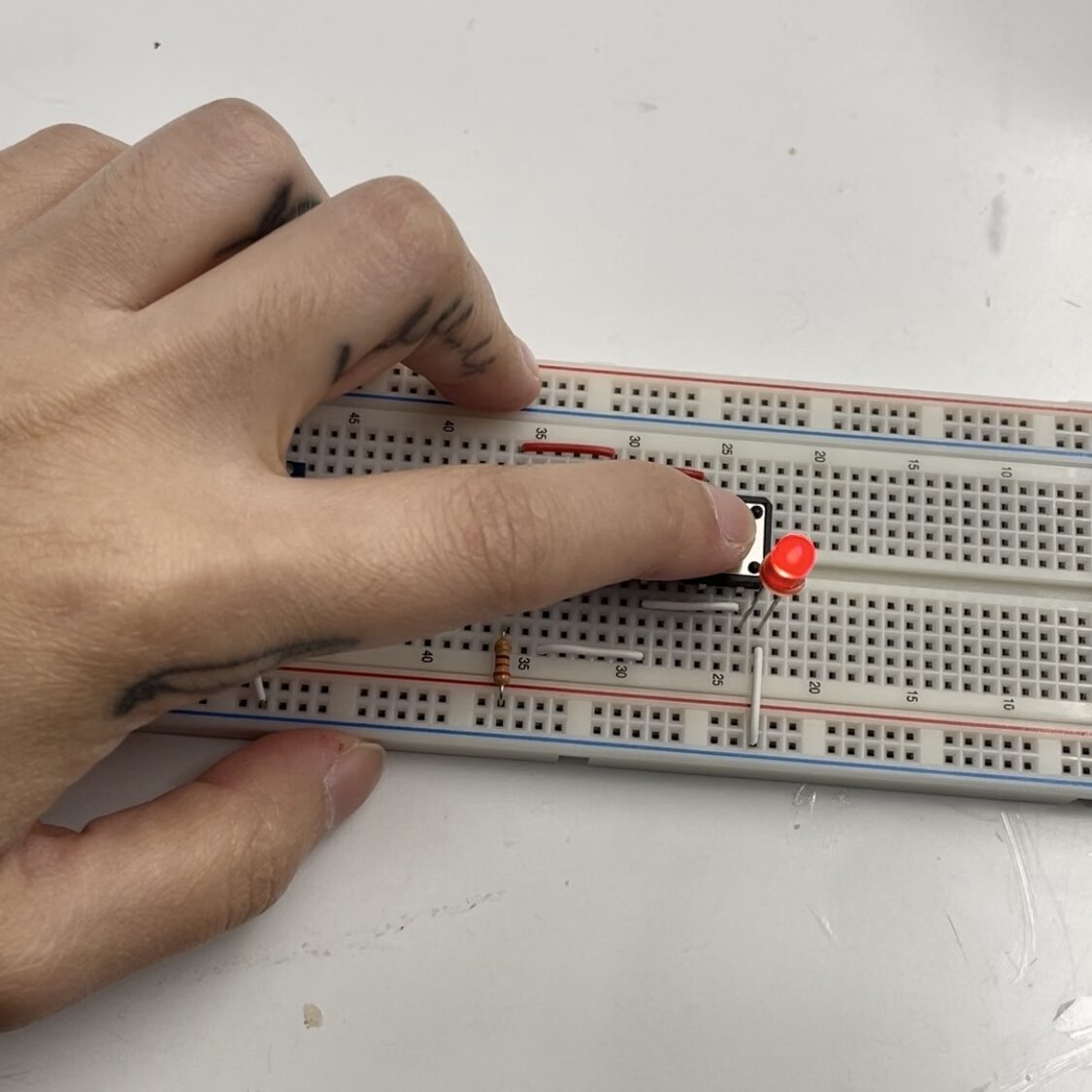
Understanding DC Power Supplies
Power was supplied to the switch-LED circuit using a 5V DC power supply
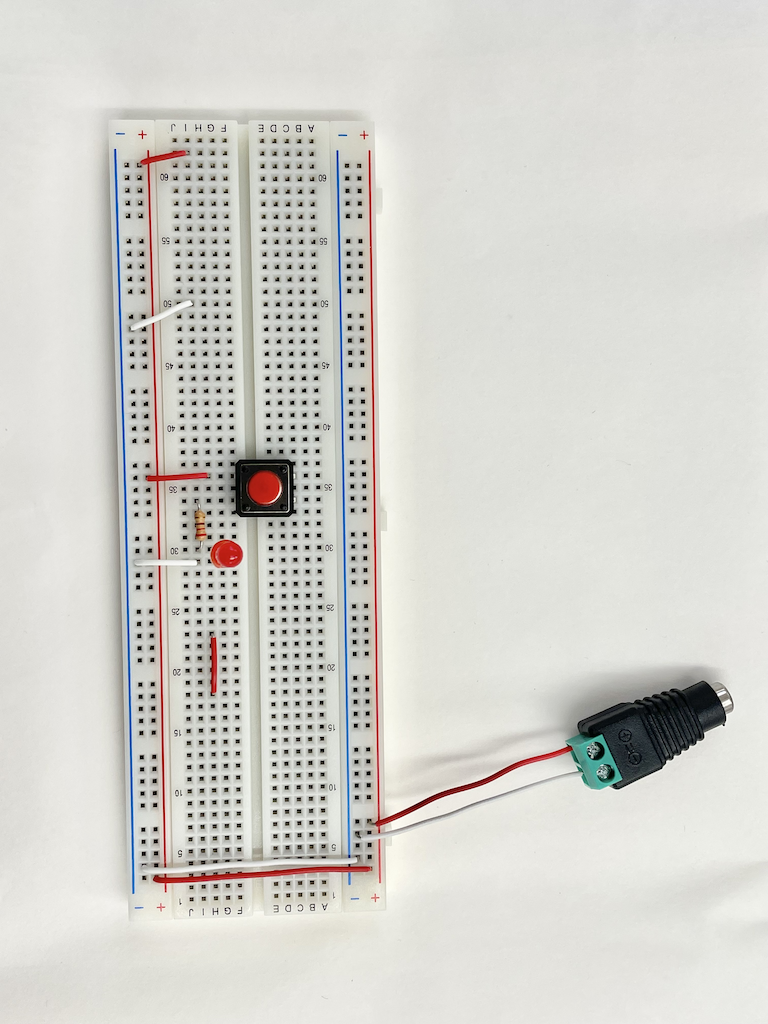
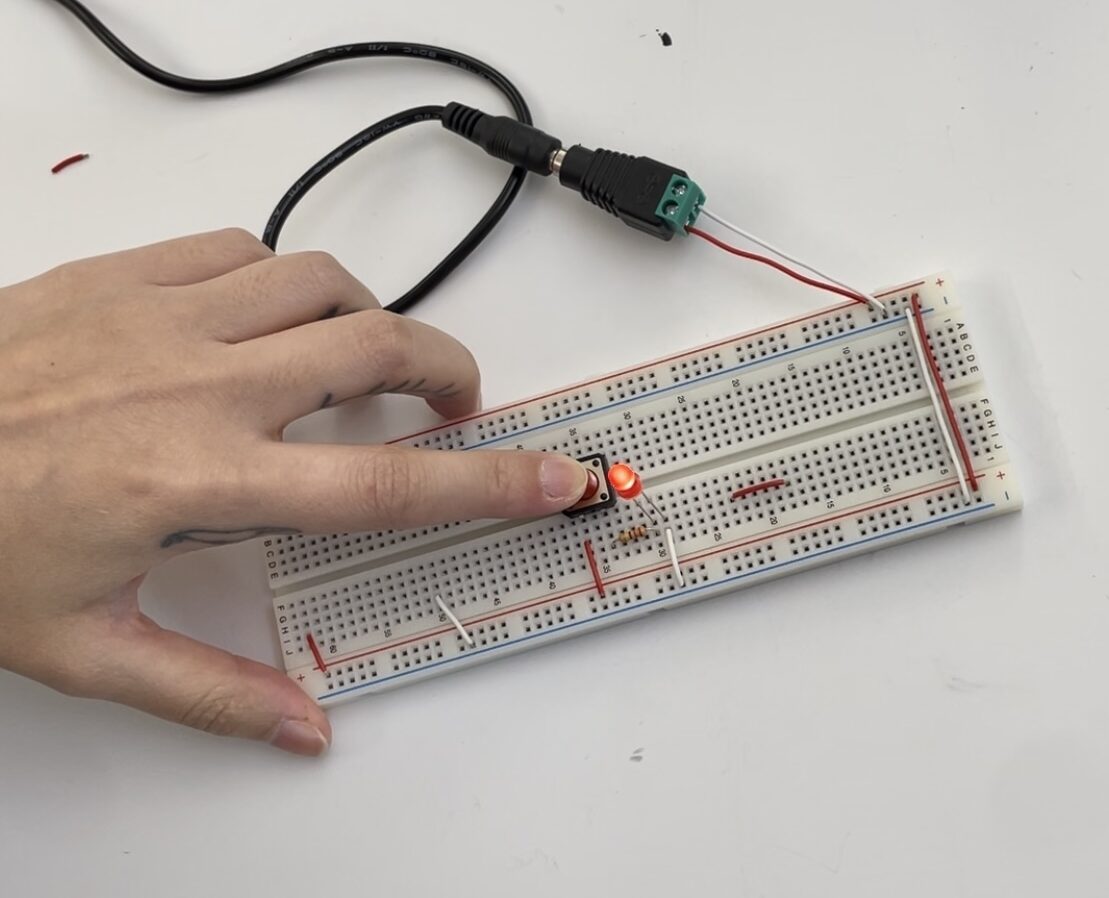
Additional Question,
- Are there any examples of using 7-21V with an Arduino Nano?
- Compared to the Arduino Uno, the Nano seems to have a lower maximum power capacity. What are the specific power limitations of the Nano?
